19 May

Predictive maintenance serves as a technique for predicting and futures failues of an equipment or any of its component. It helps to know when an equipment needs fixing or repair based on a predefined plan. Thus, it minimizes downtime, and the lifespan of an asset is maximized.
What Is Planned Maintenance System?
A planned maintenance system refers to a software system that enables maintenance operators and teams to plan necessary maintenance tasks. They are capable of requesting and scheduling tasks in sets on the basis of the requirements of each asset. Once the required work is done, they record that task as complete.
Meaning of Planned Maintenance
You have a kind of planned maintenance system in place if you have a process in place where you document and schedule any of your maintenance activities.
This kind of maintenance is carried out in order to keep a minimum equipment downtime. This often means that you have strategies set in place to get them and running all over again as soon as any of your asset breaks down.
Let’s separate planned maintenance break down into two categories:
Preventative Maintenance
The most important one is preventative maintenance.
As you can understand, just by looking at the term, it’s where you have a strong maintenance schedule in place that will enable you to address the certain issue before they occur. This is exactly the same that you do with your car on a regular basis. When you buy a car, it surely comes with maintenance or a service schedule. If you follow up on that schedule, you could end up having years of using the same car. You make sure the oil gets changed or added before its engine catches fire, and the fan belt gets replaced before it snaps. It is an easy-to-understand concept.
If you do not take care of your car and ignore your maintenance schedule, you are putting your car and your money at risk because once something bad happens, it might cost you a lot more than just changing oil, tuning up, and replacing parts.
Planned Unscheduled Maintenance
This is where you are attempting to repair or replace already broken equipment. However, the breakdown is unscheduled; it is essential to build a plan in place beforehand so as to deal with the broken machines and equipment.
Your focus should be to fix the broken equipment and get everything back to running without issues as soon as possible.
For instance, you have a shop vehicle and its fuse shorts frequently, and it turns off. It would be a wise decision to keep a spare battery or two in order to change it before anyone gets hurt.
This enables you to save time and your team from getting hurt, and it proves to be a cost-effective way to deal with failures.
Key Takeaways
- The main focus of the planned maintenance system to make sure that the equipment downtime is minimal.
- Planned preventative maintenance is when you schedule and perform maintenance before the equipment breaks down.
- Breakdowns can happen anytime, and it is possible that you are not ready for them. So you keep all the necessary equipment parts with you as spares so you could fix the issues and repair the equipment as soon as possible.
How Does Planned Maintenance Work?
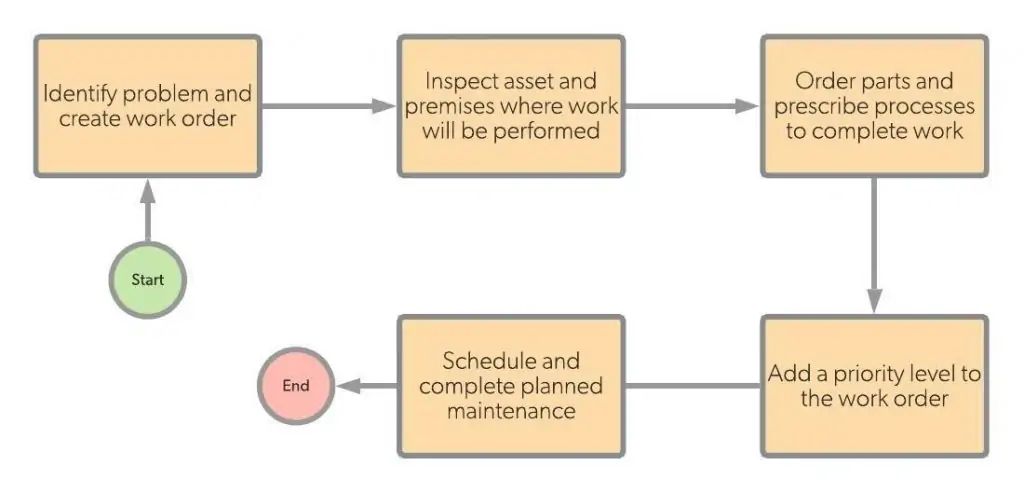
Identifying the problem and creating a work order
Planned maintenance starts with highlighting the work’s scope that needs to be completed. This is usually done in response to a work order. It can also be based on a repeating schedule. The supervisor or the operator who is responsible for detecting issues is required to send the right information to the maintenance planner. This information is consists of the details about the issue, the broken equipment, and any additional issues that are related to it.
Inspecting the premises and equipment where work is being performed
After gathering al important and required information and identifying the exact problem, the concerned personal outlines all the details of the task that needs to be performed. This also adds the scope of work, tools that re required, and whether specific materials or replacement parts will be needed. Additionally, it is important to run an inspection on the site of work, equipment, materials, and all other necessary assets, which will be affecting the required task to be completed.
Order the required parts and outline a process for completing work
It is important to decide procedures that are needed to complete the work. Items like assess requirements, shutdown procedures, and other safety precautions are essential for completing a maintenance task. Also, it is vital to outline these considerations while you are in the process of planning.
Give a priority level to the work order
Once you are done outlining the work, you need to prioritize it, and required essential materials should be ordered. The maintenance planner is responsible for handling all the tasks and ensuring that the work is ready to go after it has been scheduled.
Schedule and complete planned maintenance
When the process of planning is complete, the phase of scheduling begins. The maintenance planner can handle scheduling, or a separate individual can take over. Scheduling maintenance is an entirely separate process from the planning of maintenance. But these two depend heavily on each other to ensure the completion f preventive maintenance.
Planned Maintenance Workflow
Checklist for Planned Maintenance Program
Here are a few things to remember when making a planned maintenance program; you can call it a planned maintenance checklist.
Choosing the right people for the maintenance team
A preventative maintenance program will not be as effective as it should be without the right and skilled people to oversee and perform maintenance tasks. In terms of operating CMMS run preventive maintenance program, it is necessary to select people from top management, maintenance managers, technicians, and other staff who are skilled enough to understand how the system operates.
Setting goals for the plan of preventative maintenance
Every organization is unique in its way in terms of resources, operation, and industry. When outlining specific goals, such factors should be considered since the scope of a maintenance plan is highly dependent upon the structure and size of a company.
Gathering detailed information on equipment
Before you prepare a preventive maintenance checklist, it is essential to make yourself familiar with the equipment of your company as well as build a baseline on its usage. In order to do this, the model, the make, and serial numbers of every piece of your equipment must be documented with all the guidelines of equipment maintenance as well as any specific requirements for their installation, replacement, and repairs. Once you are done documenting, proceed with assessing a piece of equipment. For doing so, machine downtime, meantime-between-failure, cost spent on replacement, time spent by technicians, and other essential details must be recorded.
Decide upon equipment and assets to include
Once you have prepared a detailed inventory list, the next step includes making a decision regarding which equipment piece must be included in a preventive maintenance plan. Look closely on the results of the equipment baseline data for including assets that high costs of repair and replacement, assets that require regular maintenance, and assets that are necessary for the company’s success.
Create a schedule for preventative maintenance
CMMS can develop various preventive maintenance schedules based on prior equipment maintenance history., standards of maintenance for individual equipment, inspection routines, availability of technicians, location of equipment, and downtime of production. These factors help to ensure maintenance schedules that are optimal and cause minimal operation disruptions.
Monitoring costs, performance, and other Adjust and KIPs as required
Once in place for months, PMs must be monitored through the evaluation of associated cost/benefit effects. While because results may vary because of changing conditions within the activities of the company, he maintenance managers may attempt to adjust PMs as required with the focus of further enhancement of the efficiency of overall operations.
What Is Planned Maintenance In TPM?
Planned maintenance is referred to as the third pillar of TPM, and it intends to minimize the number of breakdowns to zero. It usually follows a structured approach for establishing a management system that helps to extend the reliability of the equipment cost-effectively.
Types of Planned Maintenance
Types of planned Maintenance
- Proactive types of maintenance.
- Reactive types of maintenance.
- Other types of maintenance.
Proactive Types of Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive upkeep is the most famous kind of proactive support. To begin leading preventive upkeep errands (PMs), an association doesn’t have to buy innovation in the event that it, as of now, has a CMMS. This isn’t the situation with prescient support, which requires condition observing sensors and new programming in corporations. In any case, with preventive support, the association risks over-booking upkeep assignments since errands are planned dependent on time instead of real conditions. All things considered, preventive support accomplishes 12% to 18% cost investment funds over receptive upkeep.
Predictive Maintenance
Prescient upkeep (PdM) is the thing that sagacious support groups try to have or are, as of now, executing. The significant boundary to PdM is the time it takes to actualize as opposed to the expense of the innovation itself. For example, a vibration sensor that can recognize unevenness, misalignment, and reverberation gives just expenses of around $200. In any case, the time it takes to introduce, incorporate with another support programming, and embrace a culture around isn’t time that all associations are eager to allot. For those that do distribute the time, PdM gives an 8% to 12% cost reserve funds over preventive upkeep.
Condition-based Maintenance
Condition-based support (CBM) is at the center of prescient upkeep in any case, all alone, doesn’t depend on innovation to decide the state of a benefit like PdM does. For example, a supervisor may teach an administrator to screen the state of a benefit and present a work demand when a particular condition is met. This methodology may, or may not be, as dependable as prescient upkeep. An association that has exceptionally prepared administrators may spot unsafe conditions better than an association utilizing PdM innovation that doesn’t have the foggiest idea what to search for.
Scheduled Maintenance
Booked upkeep incorporates work that is planned on a schedule for fulfillment. The most well-known sort of planned support is to schedule based preventive upkeep assignments. These are planned well ahead of time of culmination. For example, a benefit with a month to month PM has twelve occasions of booked support in a given year. Because on the grounds that upkeep is booked doesn’t mean it’s arranged. Arranged upkeep suggests that a supporting organizer or another sort of support specialist has completely anticipated parts, materials, abilities, and different assets to be accessible during the planned time window.
Planned Maintenance
Arranged support is work that is set up for ahead of time of it occurring. As per an UpKeep study, it’s additionally the most well known key execution marker (KPI) to follow. A high arranged upkeep rate shows that a support group will have assets accessible to finish work for the time/day the work is booked for. Having a high arranged support rate additionally helps help other upkeep KPIs like calendar consistence. Increasingly arranged upkeep implies progressively fruitful fulfillment of booked support.
Routine Maintenance
Routine support is a type of time-sensitive upkeep and preventive upkeep. However, a few associations separate between routine support and preventive support. They utilize the last for littler assignments (for example, cleaning) performed at higher frequencies (hourly, day by day) and the previous for bigger undertakings (for example, assessments) performed at lower frequencies (week after week, month to month, every year). Also, routine upkeep is performed by administrators, janitors, and another staff part while professionals perform preventive support. Non-routine support incorporates upkeep that is performed responsively or just when required, dependent on a benefit’s conditions.
Reactive types of Maintenance
Emergency Maintenance
Crisis support happens when a benefit requires prompt consideration so as to guard an office operational or. This is the most receptive and nosy sort of support as it pulls specialists from different occupations and brings down timetable consistence. In extraordinary conditions, crisis upkeep can interfere with an association day relying upon the extent of the fix, accessible parts, and the benefit’s degree of significance. To decrease the measure of crisis support that is both spontaneous and unscheduled, associations receive different types of proactive upkeep.
Corrective Maintenance
Restorative upkeep is inalienably part of crisis support since, when there is a crisis, something needs to be revised or fixed. Along these lines, restorative support is, for the most part, responsive. In any case, it can likewise be proactive. On the off chance that a benefit with a condition observing sensor distinguishes an issue, a work request is made, and a specialist is sent to address it. Likewise, preventive upkeep is viewed as remedial support if there is an issue to fix. This is uncommon, however, as PMs are regularly directed when a benefit is in acceptable working request.
Other types of maintenance
Deferred Maintenance
Conceded upkeep incorporates fixes and assessments that are placed into a build-up because of restricted spending plans and assets. While conceding upkeep sets aside cash in advance, the expenses of not performing significant support mix at 7% every year. Increasing costs originate from fines coming about because of missed reviews and unscheduled personal time that carries creation to a halt. By a wide margin, conceded upkeep and crisis support are the least wanted sorts of upkeep.
Total productive Maintenance
All out profitable support (TPM) is the broadest sort of upkeep that objectives more than the benefits that need to be kept up. It likewise intends to improve worker fulfillment and by and large spirit in the work environment, explicitly in assembling plants. TPM does this by generally expanding gear adequacy (OEE) and the measure of arranged support. Progressively arranged work implies more laborers have the assets they have to carry out their responsibility, which implies more significant levels of fulfillment. TPM additionally uses machine administrators to take part in the support and take responsibility for gear.
Planned Maintenance Advantages and Disadvantages
Here are some major advantages and disadvantages of planned maintenance:
Advantages
- Less hazard factor-Because the hardware and your structure is by and large consistently checked, they are at less hazard to separating without notice in this manner making a more secure workplace for representatives.
- Follows a timetable By following a calendar, you can keep to a financial plan while keeping up your structure. Likewise, you will have the option to monitor all your hardware and pinpoint times when you should supplant your gear.
- Longer hardware/building life-When gear is being checked and kept up; it will be kept in its best shape, in this manner broadening its lifetime. With normal registration on building parts, for example, funnels, boilers, and material, you’ll broaden the life of your structure also.
- Cash sparing Over time, you will see that less cash is being spent because you won’t need to supplant gear so a lot, just as managing a minute ago break downs. While there still might be some spontaneous upkeep required, the feasible hood will go down when the structure and gear are routinely checked. Property insightful, you’ll have the option to get rooftop spills before they heighten and rapidly fix them before shape and garbage happen.
- Less vitality squandering as a rule when the gear is not kept in the ideal conditions, it will deplete more vitality, climbing up your utility bill. With appropriately looked after hardware, it will be set aside your vitality and cash. While normally continued lighting and cooling/warming frameworks will likewise help diminish the vitality bill.
- Fewer interruptions With normal checks, you won’t be astounded when something turns out badly. It will be a handy solution since you will realize what should be finished. There wouldn’t be issues with regards to shutting down your property and upsetting your laborers if a huge issue were to happen.
Disadvantages
- More cash forthright When at first beginning a safeguard support plan, it will cost you more to consistently keep up the gear and the structure, than it would be if you hang tight for things to just separate.
- Over support, Because there is a standard arrangement, at times, things should not have to be checked as frequently as arranged. If so, you can change your support intend to checking the particular hardware or regions less regularly, while as yet keeping up a calendar.
- More specialists Planned support requires more laborers since customary checks are an absolute necessity. At the point when contrasted with responsive upkeep, you just need to call somebody in for an onetime fix. Rather this strategy expects laborers to be nearby and perform day by day works consistently.
Planned VS. Unplanned Maintenance
What is the planned maintenance?
With arranged support, a visit is planned to examine and support your frameworks. Arranged support will require a specialist to examine wear on the framework and can spot issues before any failure occurs.
What is unplanned maintenance?
Impromptu support happens when something is broken—regularly known as a crisis, receptive, or breakdown upkeep. This kind of support can cost 3-9 times more than arranged upkeep because of additional time, Callouts, and parts being required rapidly.
For what reason does it matter?
- Notwithstanding organization size or kind of business, the best system is to timetable and plan your support. Arranging will help diminish crisis personal time; this will lessen the expenses of parts and get out charges, thus decreasing your support costs. Advantages of arranged upkeep
- Spending arranging arranged support would permit you to anticipate expenses and level them out.
- Time and asset proficient, work timetables can be arranged ahead of time.
- Lessens vitality costs, appropriately kept up the gear, utilizes less vitality.
- Profitability, on the off chance that your organization’s frameworks are kept up, there will be less breakdown, setting aside time and cash.
Planned Maintenance VS. Preventive Maintenance
Preventive support just alike with Planned support and is arranged or booked upkeep, performed in any event, when machines or the frameworks are in the finished practical mode, to keep any breakdowns or issues from happening later on. Fundamentally, it is the same as a customary registration. While its fundamental reason for existing is to forestall breakdowns, utilizing preventive upkeep programming additionally broadens the life expectancy of the machine or resource, and increment proficiency and efficiency.
In any case, once more, it’s not as straightforward as it sounds. There is plenty of confusion that accompanied preventive support to the executives, the first being the cost: we can’t place our whole financial plan into it, correct?
Considering choices that appear to be vital for deciding which resources require support and when do they need it, seems to be very critical. That way, you can stay away from pointless or futile support and diminish costs.
Major Advantages of the Planned Maintenance
Reduced costs of maintenance
Planned maintenance paves the way for amazing opportunities to minimize maintenance costs. By setting up planned preventative maintenance, minor problems and repairs can be fixed before they become causes of big and expensive failures.
Long asset life
When assets are getting routine services, they end up working for years. Maintenance of equipment and keeping them operating in suitable conditions are te two main reasons for their extended lives.
Enhanced workplace safety
It is very important to prevent equipment from failures. Because if it does, it will require a huge sum of money to be repaired. But it is better to maintain a safe distance from equipment to prevent any disaster from happening.
Improved culture of the workplace
Planned maintenance helps to reduce equipment downtime and also employee downtime. Planning tasks of preventative maintenance and stopping unfortunate equipment failures from occurring helps to keep your employees active, motivated, and productive.
Minimizes Downtime
If you leave any equipment unattended, it will eventually lead to failures and unexpected breakdowns that will affect overall production processes. Fixing the equipment will be expensive as well as it will delay the process of production. Planned maintenance availability will not only help you to prevent breakdowns and failures from happening but will also enable you to enhance your productivity.
Planned Maintenance – Using Computer Systems
Since tasks of a planned maintenance program are performed regularly, they can be helpful to collect information that can be fed to a computer system so as to track the needs of maintenance, as well as for scheduling tasks themselves. However, it is essential to remember that you can only save information on a computer system. It cannot design your system for planned maintenance, nor can it determine how the work will be done.
While working with the department of production and often, with a service representative from the manufacturer’s side, the maintenance of equipment that needs regular scheduling must be identified, and a proper planned preventative maintenance schedule should be developed. It is essential to decide a method for measuring the effectiveness of the planned maintenance to evaluate the overall system as well as individual tasks.
One major thing that the planned maintenance provides help with is ensuring that the equipment is installed correctly and in compliance with their specifications and running active checks to identify any performance problems. This helps to find out the potential problems before they turn into big failures.
EcoDocs is a cloud-based CMMS software that organizes, tracks, and schedules your quality, compliance, and maintenance management tasks, making your workers more agile and productive.



Ecodocs